Are you seeking a holistic approach to healing that delves deep into the mind-body connection? Somatics, a diverse set of therapeutic practices, might just be the answer. In this blog post, we will guide you through the roots, benefits, and techniques of somatic therapy, helping you explore ways to enhance your overall well-being and address various physical and emotional concerns.
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
Somatics is a form of therapy that seeks to improve physical and emotional wellbeing by addressing the connection between mind and body.
A variety of somatic exercises, such as stretching, Feldenkrais, yoga or pilates can be used to promote self-awareness and reduce tension.
Integrating somatic practices into daily life has been shown to lead to improved mental health outcomes.
Exploring the Roots of Somatics
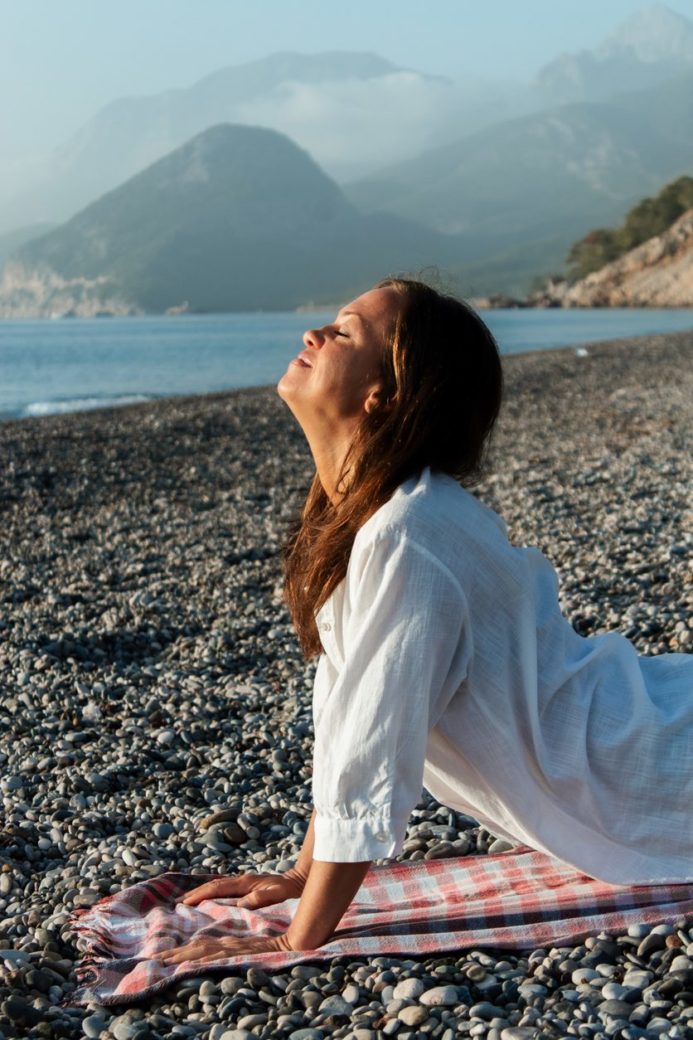

The term “somatics” emerged as a way to describe a broad spectrum of mind-body practices that focus on internal awareness and mindful movement. These practices, which originally developed from various western body-mind disciplines and bodily arts, share a common ground in promoting self-awareness and healing through physical sensations and movement. Some well-known examples in the field of somatic education include the Feldenkrais Method and Clinical Somatic Education.
A brief history of somatic practices reveals a rich tapestry of techniques, each one uniquely honed to address specific aspects of the mind-body connection. Interestingly, somatic education intersects with the world of dance, where dancers often utilize somatic techniques to enhance their sensory experience and build a strong connection with their bodies.
Somatic practices, including somatic therapies, have emerged as a pivotal component of contemporary healing, therapy, and athletic training.
The Mind-Body Connection in Somatics
Somatic therapy illuminates the intricate relationship between our emotions and physical sensations. By addressing this connection, somatic techniques aim to release trapped emotions and alleviate physical symptoms of emotional distress, such as muscle tension. The primary goal of somatic therapy, encompassing clinical somatic education, revolves around pain alleviation and stress symptom mitigation through emotional intensity reduction.
Various techniques used in somatic therapy include:
Acupressure
Hypnosis
Breathwork
Dance
These techniques, including body psychotherapy, are employed to foster a connection between the mind and body and often complement traditional mental health counseling, providing a holistic approach to healing. Somatic therapy has shown potential in addressing emotions associated with anxiety, chronic distress, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
Unraveling Chronic Pain with Somatic Techniques
Clinical Somatics, a type of somatic technique, focuses on the relationship between the mind and body, promoting self-awareness and understanding of one’s physical and emotional state. By teaching individuals how to alter their movement, posture, and body language, somatic exercises can help diminish pain and improve overall well-being.
Addressing chronic pain through Clinical Somatics involves re-educating learned muscular patterns through slow, conscious movements. This process targets full-body patterns of posture and movement, allowing individuals to break free from deeply ingrained habits that cause harm to the body. Muscle memory, which refers to how our nervous system facilitates movement and posture, often plays a significant role in chronic pain, joint degeneration, and recurring injuries.
For enduring alteration in the nervous system and to alleviate chronic pain, daily practice of somatic stretches is recommended. Consistent practice allows individuals to gain an understanding of their muscle sensations, ultimately leading to tension relief and pain reduction over time.
Somatic Practices for Mental Health and Trauma Recovery
Somatic practices prove instrumental in mental health and trauma recovery, aiding individuals to process buried emotions and trauma through body-based therapies. By enhancing emotional awareness and addressing trauma symptoms, techniques such as:
Breathwork
Mindfulness
Dance
Other mindful movement techniques
We offer a supportive path to healing, designed to relieve pain effectively.
Numerous case studies have demonstrated the effects of somatic practices on mental health. For example, one study reported positive effects of Somatic Experiencing (SE) on comorbid depression, while another study found that mindfulness alone improved clinical outcomes for less severe cases of depression. These studies provide evidence of the beneficial effects of somatic practices on mental health.
Diverse Somatic Exercises for Improved Well-Being
A wide range of somatic exercises, such as somatic stretching and the Feldenkrais method, can lead to improved mobility, reduced pain, and enhanced overall well-being. These exercises focus on promoting body awareness, releasing tension, and correcting imbalances through somatic movement, leading to benefits like improved balance, coordination, and range of movement, especially in the elderly population.
Somatic stretches, such as the Iliopsoas exercise and the Carpal Tunnel Exercise, are designed to increase awareness of muscles and their surrounding areas while facilitating the release of tension. Through daily practice of these exercises, individuals can deepen their understanding of their muscle sensations and progressively experience the benefits of tension alleviation and pain reduction.
In addition to these specific stretches, other somatic exercises like yoga, pilates, and dance education can also be incorporated into one’s daily routine. These diverse exercises cater to different needs and preferences, allowing individuals to customize their somatic practice for optimal well-being.
Finding a Qualified Somatics Practitioner
For harnessing the complete benefits of somatic therapy, finding a seasoned and trained practitioner to guide through the process remains a priority. Collaborating with a qualified practitioner, particularly during the initial stages or when dealing with existing injuries, can help ensure the most suitable exercises are chosen for your specific needs.
Although finding an experienced somatic therapist can be challenging due to the limited number of trained professionals, resources like the US Association for Body Psychotherapy’s Find a Therapist search tool can help you locate a qualified practitioner.
If you’re unable to find a local somatics practitioner, consider starting with more renowned forms of somatics, such as yoga or pilates, as instructors may be able to provide recommendations for related practices in your area.
Integrating Somatics into Daily Life
The integration of somatic practices into daily life can catalyze enduring enhancements in physical and mental health. Regular practice of somatic exercises can result in:
Better sleep
Increased flexibility
Enhanced balance
Reduced stress and anxiety
Improved body awareness
The timeframe for observing the effects of daily somatic practices varies from person to person; some may notice results within the first week, while others may take a few days or weeks. Consistency is key, and practicing for about 10-15 minutes daily can be advantageous.
Somatic practices are conducive to a home setting, conducted independently or via online sessions with a certified somatic educator. By integrating these practices into your daily routine, you can work towards a healthier and more balanced lifestyle. Some examples of somatic practices include:
Breathwork exercises
Mindful movement, such as yoga or tai chi
Body scans and body awareness exercises
Progressive muscle relaxation
Meditation and mindfulness practices
These techniques can help address both physical and emotional concerns with the help of somatic techniques.
The Science Behind Somatics
While somatic therapy currently lacks extensive research backing, studies that have been conducted show positive results in addressing trauma symptoms, pain relief, and improved mobility. Somatic therapy’s limited research base places it behind cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and related techniques in terms of understanding, application, and supporting research.
Recent studies on the efficacy of somatic therapy have shown promising results. One study conducted on Somatic Experiencing (SE) indicated that it may be a viable therapy method for PTSD. Another study suggested that somatic therapy may address symptoms of depression, anxiety, and pain. Although the existing research is limited, it points to the potential benefits of somatic therapy.
Even with limited research, somatic therapy’s popularity burgeons as a potential alternative to conventional mental health counseling. The positive results from existing studies provide a solid foundation for further exploration, potentially leading to a better understanding of the mind-body connection and the therapeutic potential of somatic practices.
Learn more, visit What is somatic therapy?
Summary
In conclusion, somatic therapy offers a holistic approach to healing that delves deep into the mind-body connection. With roots in various therapeutic practices and techniques, somatic therapy focuses on addressing physical and emotional concerns through increased internal awareness and mindful movement. By incorporating somatic practices into daily life, individuals can experience lasting improvements in physical and mental health, including better sleep, flexibility, and balance.
While the research on somatic therapy is limited, existing studies show promising results in addressing trauma symptoms, pain relief, and improved mobility. As we continue to explore the potential benefits of somatic therapy, embracing the mind-body connection becomes an increasingly important aspect of our journey towards holistic well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does Somatics do?
Somatics is a field of movement studies and bodywork that utilizes various mind-body techniques to help people release damaging, pent-up emotions from the body. It can result in improvements in posture, flexibility, range of motion, and balance, as well as a better connection between the mind and body.
What is the difference between yoga and Somatics?
Unlike yoga which may feel like a struggle and require pushing yourself to your limits, Clinical Somatics works to extend movement without straining or forcing anything, creating an overall sense of relaxation.
Is somatic therapy legitimate?
Evidence suggests that somatic therapy is legitimate as long as a patient is receiving evidence-based care.
What is the primary focus of somatic therapy?
Somatic therapy emphasizes the relationship between emotions and body sensations, aiming to liberate suppressed feelings and diminish physical manifestations of distress, such as muscle tension.
How does Clinical Somatics address chronic pain?
Clinical Somatics uses full-body posture and movement patterns to re-educate the muscular patterns responsible for chronic pain, allowing users to consciously reduce their discomfort.