Imagine a world where managing diabetes becomes less of a daily burden and more of a seamless integration into your life, thanks to continuous glucose monitors. Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) brings us closer to that reality, revolutionizing diabetes management by providing real-time updates on blood glucose levels. In this blog post, we’ll explore the ins and outs of CGM systems, their benefits, and how they compare to traditional blood glucose meters. We’ll also discuss the future of diabetes technology and provide practical tips for optimizing continuous glucose monitor use to improve your quality of life.
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) systems provide diabetics with the information necessary to effectively manage their condition and prevent complications.
CGM devices offer greater accuracy, convenience, and continuous monitoring compared to traditional glucose meters.
Practical tips such as calibration and alarm/alert management can help optimize CGM use for improved diabetes management.
Understanding Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM)
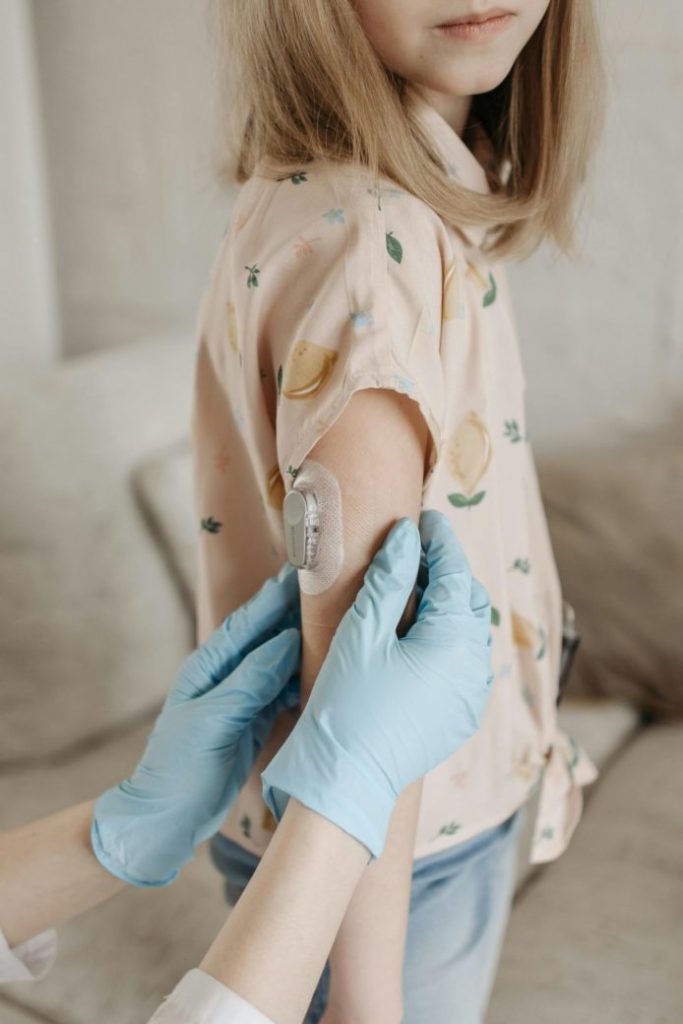
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) systems offer persistent monitoring of blood glucose levels, providing valuable insights for diabetes management. By understanding how continuous glucose monitor work, diabetics can make informed decisions about diet, exercise, and medication, which helps maintain their glucose levels within a healthy range and prevent complications.
CGM devices are an invaluable tool for individuals with diabetes, as they can identify trends and patterns that help both patients and healthcare professionals manage the condition more effectively.
How CGM systems work
CGM devices measure glucose levels in the interstitial fluid using a tiny sensor placed under the skin. This sensor wirelessly transmits glucose data to a smartphone app or receiver, allowing users to monitor their glucose levels in real-time. Continuous monitoring enables CGM users to take informed actions for their diabetes management, like adjusting insulin dosage or modifying lifestyle habits to sustain a healthy glucose range.
Some CGM systems utilize disposable sensors that are inserted just beneath the skin, while others employ implantable sensors that are placed internally. Regardless of the sensor type, the primary goal of these devices is to provide accurate, real-time glucose level data to help improve diabetes management and overall health outcomes.
Types of CGM devices available
There are various types of CGM devices available, each offering unique features and benefits.
Real-time CGM devices provide:
Continuous information, alerts, and alarms
Data tracking
Improved accuracy
Integration with apps and devices
Customizable settings
Intermittent-scan CGM devices, on the other hand, use a combined glucose sensor and reader device to measure and store glucose data. The user simply scans the device with the reader to access the data, offering convenience and cost-effectiveness compared to continuous real-time CGM devices.
Data collection CGM devices, also known as continuous glucose monitors, differ from other glucose monitoring devices in the following ways:
They provide continuous monitoring of glucose levels
They transmit collected data wirelessly to a receiver or smartphone
They generate complex data streams for analysis and interpretation
These devices enable users to track glycemic activity and understand the impact of various factors on their glucose levels, thereby guiding their decisions about diabetes management.
The Importance of Blood Glucose Management in Diabetes
Effectively managing blood glucose is paramount for people with diabetes mellitus to avoid complications and tailor treatment plans to suit their needs and lifestyle factors. Proper blood glucose control can help prevent health complications such as nerve damage, kidney failure, and heart disease.
Understanding how much insulin to administer is crucial for maintaining stable blood sugar levels.
Preventing complications
Maintenance of blood glucose levels within the specified range can significantly lower the risk of serious health complications for individuals with diabetes, such as low blood sugar levels. For example, tight glycemic control can prevent or delay the development of neuropathy, a condition caused by high blood sugar levels that damages nerves throughout the body.
Similarly, keeping blood glucose levels in check can help diminish the risk of kidney damage and failure, as well as reduce the chances of heart damage and associated diseases.
Learn more, visit Regulation of Blood Glucose.
Personalizing treatment plans
CGM systems can play a pivotal role in tailoring treatment plans for individuals with diabetes. By providing real-time and continuous data on blood glucose levels, healthcare providers can make informed decisions and personalize treatment plans based on the patient’s unique needs and lifestyle.
CGM also empowers patients to track their glucose levels, recognize patterns, and make proactive modifications to their treatment plan, ultimately leading to better diabetes management and overall health.
Comparing CGM to Traditional Blood Glucose Meters

CGM systems offer distinct advantages over traditional blood glucose meters in terms of accuracy, convenience, and continuous monitoring. While traditional glucose meters provide a single measurement of blood sugar levels at a specific time, CGM devices measure glucose levels in interstitial fluid every few minutes, offering real-time updates and a more complete picture of glucose levels and trends.
Accuracy and convenience
CGM devices provide more accurate and continuous data compared to traditional glucose meters. Mean Absolute Relative Difference (MARD) values in studies indicate a range of 7.8% to 12.2% for CGM devices and 4.4% to 13.4% for traditional blood glucose meters, although these values may vary between specific devices.
Moreover, CGM devices help prevent hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia by recording the speed and direction of changes in glucose levels, ultimately providing better diabetes management.
Cost and insurance coverage
Although CGM systems can be more expensive than traditional glucose meters, insurance coverage varies and may help offset the cost for some individuals. The cost of CGM systems ranges from $100 to $300 per month, depending on the brand and pharmacy, while traditional glucose meters are typically available over the counter for around $40 or less. However, it is important to investigate your health insurance plan or Medicare coverage to determine if CGM costs will be covered.
Addressing Common Concerns and Challenges with CGM Use
Common concerns and challenges with CGM use include sensor placement, skin irritation, and interpreting the data for informed decision-making.
Addressing these issues can help users optimize their experience with CGM and improve diabetes management results.
Sensor placement and skin irritation
Proper sensor placement and care can help minimize skin irritation and ensure accurate readings. To optimize placement, follow these steps:
Clean the skin with oil-free, antimicrobial soap, and dry thoroughly.
Gently exfoliate oily skin.
Trim hair in the area if needed.
Avoid using lotions and oils on the skin before sensor placement.
By following these steps, you can ensure proper sensor placement and minimize skin irritation.
Additionally, consult the manufacturer’s guidelines for approved sensor placement locations and follow their recommendations for sensor replacement frequency.
Data interpretation and decision-making
Understanding and interpreting CGM data can be overwhelming, but working with a healthcare professional can help users make informed decisions about their diabetes management. Some crucial steps in responding effectively to CGM alerts and alarms include:
Personalizing alert settings
Verifying readings with a blood glucose meter
Understanding trend arrows
Setting appropriate alert levels
By following these steps, users can better understand and utilize their CGM data for effective diabetes management.
By adopting these strategies, users can make the most of their CGM system and improve their quality of life.
The Future of Diabetes Technology: Artificial Pancreas and Automated Insulin Delivery Systems
The future of diabetes technology includes artificial pancreas systems and automated insulin delivery, which combine CGM data with insulin pumps for improved glucose control. These advanced systems mimic the function of a healthy pancreas, regulating blood glucose levels and automating insulin delivery to enhance diabetes management and patient outcomes.
How artificial pancreas systems work
Artificial pancreas systems use CGM data, insulin pumps, and software algorithms to estimate glucose levels and deliver insulin accordingly. These systems imitate the glucose-regulating activity of a healthy pancreas, closely monitoring blood glucose levels and automatically adjusting insulin delivery.
Artificial pancreas systems, which automate insulin delivery through an insulin pump based on real-time glucose levels, can enhance diabetes management and lighten the burden on patients.
Current research and clinical trials
Current research and clinical trials are focused on improving the effectiveness, comfort, and applications of artificial pancreas systems for diabetes management. Studies are being conducted on closed-loop systems, dual-hormone systems, and fully-automated insulin delivery systems, aiming to develop more sophisticated technologies and algorithms to optimize blood glucose management and lessen the burden on patients.
With these advancements, supported by organizations like the American Diabetes Association, the future of diabetes management looks promising, offering improved quality of life for individuals with diabetes.
Practical Tips for Optimizing CGM Use
For optimal use of your CGM system, it’s important to adhere to practical tips for correct calibration and effective management of alarms and alerts. By doing so, you can ensure the device’s accuracy, optimize its performance, and enjoy a more seamless experience.
Calibrating your CGM device
For accurate readings and optimal performance, you should calibrate your CGM device as per the manufacturer’s guidelines. By comparing CGM glucose readings with fingerstick blood glucose measurements, users can ensure that the CGM readings are consistent with their actual glucose levels, maintaining accuracy over time.
Some manufacturers recommend calibrating the device at least every 12 hours, while others suggest calibrating 2 to 3 times per day for optimal accuracy.
Managing CGM alarms and alerts
Managing CGM alarms and alerts can help users stay informed about their glucose levels without feeling overwhelmed. Personalizing alert settings, verifying readings with a blood glucose meter, understanding trend arrows, and setting appropriate alert levels can ensure that users receive important glucose notifications while silencing unnecessary alerts.
Effective management of CGM alarms and alerts can enhance users’ diabetes management and overall quality of life.
Summary
In conclusion, Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) systems offer a revolutionary approach to diabetes management, allowing individuals to track their glucose levels in real-time and make informed decisions about their treatment plans. By understanding how CGM devices work, comparing them to traditional glucose meters, addressing common concerns, and embracing the future of diabetes technology, users can optimize their CGM experience and improve their quality of life. Embrace the power of CGM and take control of your diabetes management journey today.
Frequently Asked Questions
How much does a CGM cost?
A CGM system can cost around $1,000 initially and up to several thousand dollars a year, depending on your provider and health plan. Sensors and transmitters typically cost around $100-$300 per month, while special pricing programs may offer CGMs for as low as $89/month.
What is the cheapest CGM?
The cheapest CGM available is the FreeStyle Libre 2 from Abbott, which is typically up to 70% less expensive than other devices and can cost around $65 for the reader and $0 to $60 for the sensors monthly.
How much does FreeStyle Libre 2 cost per month?
Most commercially-insured or privately-insured individuals pay no more than $40 per month for FreeStyle Libre 2 sensors, with reader costs typically up to $65. Actual cost may vary depending on your insurance coverage.
What are the main benefits of using a CGM system for diabetes management?
The main benefits of using a CGM system for diabetes management are continuous monitoring, real-time updates, and valuable insights that enable users to make informed decisions and maintain their glucose levels within a healthy range.
How often should I calibrate my CGM device for optimal accuracy?
It is recommended to calibrate your CGM device at least every 12 hours, or up to 2-3 times a day for optimal accuracy.