The Mullein plant, known scientifically as Verbascum, is a multifaceted herb revered for its medicinal properties and striking appearance. This practical guide takes you through the basics of mullein – its identification, ecological impacts, and how to grow and use it for health benefits. Whether you’re an aspiring herbalist or a curious gardener, uncover the diverse world of mullein with us.
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
Mullein is a resilient plant that thrives in disturbed soils and has invasive characteristics, which can lead to the displacement of native species and alteration of natural habitats.
Cultivation of mullein in gardens requires dry, sandy, and slightly alkaline soils with full sun exposure, and while regular fertilization isn’t essential, occasional application can improve growth.
Mullein has traditional medicinal applications, particularly as a respiratory aid and for ear treatment options, with simple home preparations like teas and oils, but it can have side effects and interact with medications.
Exploring the Mullein Plant
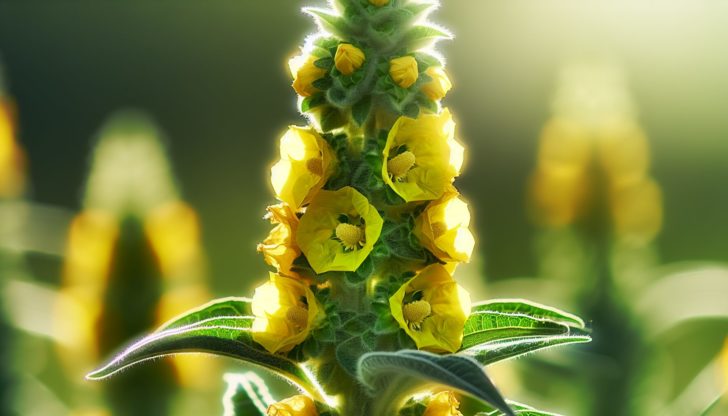

Mullein, a member of the Verbascum genus, boasts over three hundred species. These large biennial or perennial flowering plants originate from the northern temperate regions of Europe, West and Central Asia, North Africa, and North America. Recognizable by their elongated terminal flower spikes, they exhibit a range of flower colors such as white, pink, lavender, purple, and, most commonly, yellow.
You might be curious about how to identify this plant and where it grows. To answer these questions, let’s proceed to our next sections, which focus on the identification of mullein and an understanding of its habitat and growth.
Recognizing Mullein
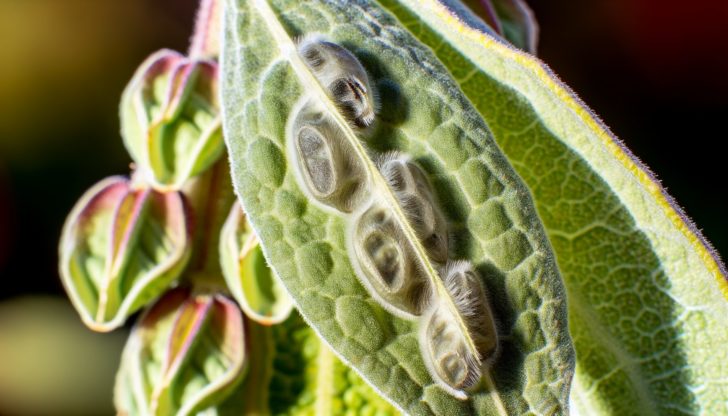

Recognizing mullein is an exercise in appreciating the details of nature. Mullein plants are:
Biennial
Covered in hair
Can reach heights ranging from two to seven feet
Their mullein leaf forms a substantial rosette at the plant’s base
Their stems are distinguished by tall flower stalks.
The small, yellow flowers, densely grouped on the tall flower stalks, are a telltale sign of this unique parent plant. Having identified the plant’s features, including the flower stalk, the next step is to find out where these fascinating plants grow.
Habitat and Growth
Mullein plants are survivors. They flourish in impoverished to average soil disturbed by human activities or natural events, demonstrating resilience to drought and abundant seed production capabilities. These plants are drawn to well-lit disturbed soils, rapidly germinating and growing from the long-lasting seeds in the soil seed bank.
The most commonly used type in commercial applications is common mullein (Verbascum thapsus). But while mullein may be a hearty grower, it also has a darker side: its invasive nature.
The Invasiveness of Mullein
While the mullein plant can be a valuable addition to a garden, its invasive nature can pose challenges. It readily adapts to various site conditions and proliferates unchecked, posing a threat to natural meadows and forest openings. Its rapid spread can be attributed to its ability to grow faster than native plants, its production of abundant and long-lasting seeds, and its potential to be spread by human activity.
The implications of this rapid spread and its control measures need to be understood. We will examine these aspects in the following sections, discussing the spread and control of mullein, along with its biological impact.
Spread and Control
The spread of mullein, particularly in regions with suboptimal soil conditions that have been disrupted by human activities or natural events, is swift and tenacious. The plant produces numerous seed capsules, which release mullein seeds that can remain viable in the soil for many years. Control measures involve the eradication of undesirable mullein plants from disturbed areas, with the most effective approach being hand-pulling the plants, particularly before the flowers set seed.
Seeds disperse mechanically, mainly during autumn and winter, when seeds fall into the parent plant’s vicinity, leading to proliferation. As seeds germinate, it’s essential to understand the ecological effects of this spread.
Biological Impact
The biological consequences of mullein invasion are profound. Mullein can displace native species, form dense stands, alter natural successional processes, and access soil moisture at the detriment of native plants. However, it also contributes organic matter to the soil through the decomposition of its leaves, serving as a slow-release fertilizer. Mullein also enhances carbon sequestration in soils, facilitates soil formation and retention, and promotes the growth of beneficial soil organisms.
Having discussed the invasiveness of mullein and its impacts on agricultural crops, our focus now shifts to the cultivation of the entire plant in the garden, considering the challenges posed by invasive plants.
Cultivating Mullein in Your Garden
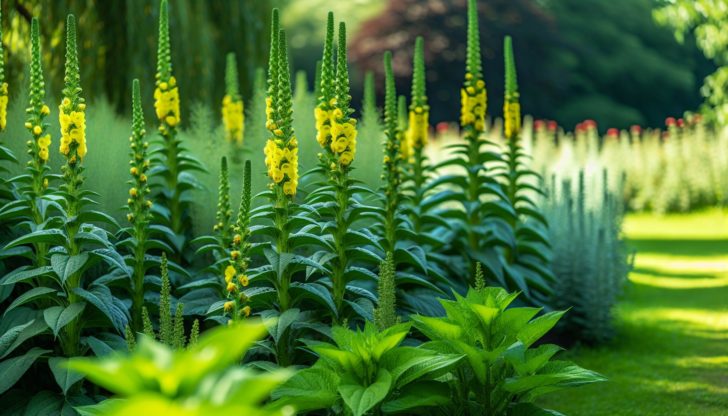

Growing mullein in your garden can be an enriching experience, as it not only adds visual interest but also offers medicinal benefits. Cultivating mullein necessitates dry, sandy soils, a growing season of 140 days or more, and adequate rainfall. Mullein prefers dry and slightly alkaline soil conditions.
You might be wondering about the sunlight requirements and watering frequency for your mullein plants. Let’s examine the specifics of soil and sunlight needs, along with watering and fertilization practices.
Soil and Sunlight Needs
Mullein thrives in a diverse range of soils, such as sandy, rocky, and particularly well-drained soil. It flourishes in well-draining, poor to average, slightly alkaline soil, and favours soil with a pH between 6.0 and 7.0, which is slightly alkaline. As for sunlight, mullein thrives in sunny locations and necessitates full sun exposure on a daily basis for optimal growth.
Next, we will discuss the watering and fertilization needs of mullein plants.
Watering and Fertilization
Mullein plants have the following care requirements:
Low water requirements, and it is advisable to allow the soil to dry out between watering
Increased requirement for water during the spring, summer, and early fall to ensure a consistently moist soil environment
Regular fertilization is not deemed essential, but the application of a general-purpose fertilizer once or twice a season can promote improved growth.
Equipped with the knowledge of cultivating mullein, the next step is to discuss harvesting.
Harvesting Mullein Flowers and Leaves

Harvesting mullein flowers and leaves at the right time can maximize the benefits you reap from this remarkable plant. The optimal time for the harvest of mullein flowers and leaves is during the summer when the plant is in bloom. But when exactly should you harvest, and what techniques should you use?
Best Time to Harvest
Harvesting mullein at the appropriate time ensures the full realization of its benefits. The medicinal properties are most potent, and the plant is at its peak for utilization during the spring and summer, before the plants initiate their flower stalks.
As for the flowers, the ideal time is during the summer when the plant is in bloom. But how should you go about harvesting?
Techniques for Harvesting
Harvesting mullein requires a gentle touch and the right technique. Here’s how to do it:
When harvesting mullein flowers, gently pull them off the plant on the day they bloom, starting from the bottom of the flower spike and moving upwards.
To effectively harvest mullein leaves, use pruning shears or sharp scissors to cut the stalks and remove the leaves.
Always practice mindful and sustainable gathering methods.
Having discussed harvesting, we now turn to the medicinal applications of mullein, including the use of moth mullein.
Mullein’s Medicinal Applications
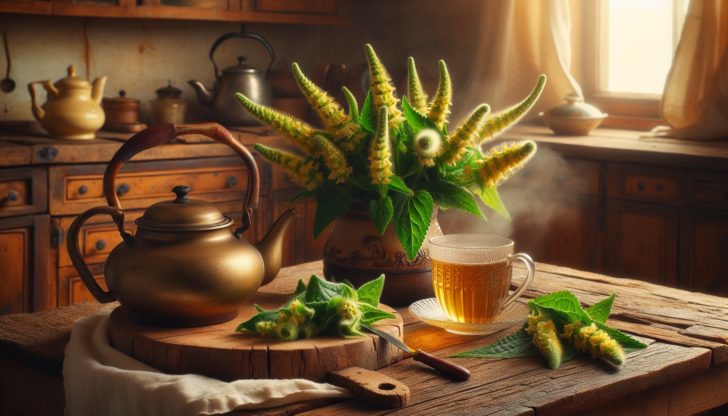

Mullein offers a plethora of medicinal benefits. Its leaves and flowers have been used traditionally for a variety of therapeutic purposes, including:
treating respiratory conditions
soothing coughs and sore throats
relieving congestion
reducing inflammation
easing ear infections
But how exactly does mullein help with these conditions?
Respiratory Aid
Mullein has a long history of use for respiratory issues. Consuming mullein tea provides relief for various respiratory problems such as sore throat, cough, colds, hoarseness, and bronchitis, and improves upper respiratory issues including dry coughs, sore throats, general hoarseness, and tonsillitis.
But what about ear infections?
Ear Treatment Options
Mullein is also effective in addressing the pain and inflammation commonly associated with earaches. Mullein oil is frequently utilized for alleviating the pain and inflammation linked to earaches. Research has indicated that herbal ear drops containing mullein can be equally efficacious as traditional ear drops for ear pain.
Next, we’ll discuss how to prepare mullein remedies at home.
Preparing Mullein Remedies at Home
Mullein remedies can be easily prepared at home. You can make a soothing tea from the leaves and flowers, or you can create mullein oil for ear treatments and other applications.
But how do you go about preparing these remedies?
Making Mullein Tea
Making mullein tea at home is a simple process. To make the herbal infusion, pour 1 cup of boiling water over 1–2 teaspoons of dried leaves or flowers and allow it to steep for ten to 15 minutes. Mullein tea offers several potential health benefits, such as its capacity to aid in expelling excess mucus, combat viral infections, decrease inflammation, alleviate sore throat and cough, and provide cellular protection.
Learn more, How to Make Mullein Tea.
Next, we will talk about how to craft mullein oil.
Crafting Mullein Oil
Crafting mullein oil involves the following steps:
Infuse fresh or dried mullein flowers in olive oil.
Steep the flowers in the oil for approximately 4 weeks.
Strain the oil to remove the flowers.
Transfer the oil to a clean, dark glass bottle for storage.
Like any herbal remedy, potential side effects and precautions should be considered, which we’ll cover in the following section.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions
While mullein has several benefits, it is important to understand the potential side effects and precautions associated with its use. Certain individuals may encounter an itchy, allergic rash referred to as contact dermatitis from certain species of mullein. Mullein has the potential to interact with certain medications and pre-existing medical conditions.
Understanding Risks
Understanding the risks and potential side effects of using mullein is crucial for safe usage. Mullein is generally deemed safe with few instances of side effects. However, it can interact with certain medications, possibly reducing the effectiveness of antidiabetic drugs and enhancing the effects of sedatives.
Who Should Avoid Mullein
Certain individuals should exercise caution or refrain from using mullein. Pregnant or breastfeeding women, as well as individuals with specific health conditions, should exercise caution or refrain from using mullein due to the lack of safety information and the potential impact on medical conditions and medication interactions.
Next, we will examine the role of mullein in attracting and supporting wildlife.
Attracting Wildlife with Mullein
In addition to its medicinal uses, mullein plays a vital role in supporting biodiversity. It attracts a diverse array of wildlife, including pollinating insects and seed-eating birds.
But how exactly does mullein serve as a pollinator-friendly plant and a shelter and food source?
Pollinator-Friendly Plant
Mullein is a boon for pollinators. Its tall flower stalks and fuzzy leaves attract a variety of pollinators, providing a rich source of pollen and nectar. Mullein plays a significant role in the life cycle of pollinators by aiding in their nutrition and the pollination process.
Shelter and Food Source
Not only does mullein attract pollinators, but it also provides shelter and food for various wildlife species. The large fuzzy basal leaves offer refuge for small insects during the winter, and the seeds are consumed by overwintering songbirds.
Certain birds, such as goldfinches and indigo buntings, even use the soft leaves for lining their nests.
Summary
In conclusion, the mullein plant, though often overlooked, is a treasure trove of benefits. From its medicinal properties to its ecological role, mullein offers a wealth of benefits. Whether you’re looking to soothe a sore throat, alleviate ear pain, or attract wildlife to your garden, this versatile plant has something to offer. As with any plant, it’s important to understand its potential side effects and precautions to ensure safe usage. So the next time you come across this enchanting plant, take a moment to appreciate its unique characteristics and the plethora of uses it holds for us and the environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
Where does mullein grow?
Mullein is commonly found in neglected meadows, pasture lands, along roadsides, wood edges, and forest openings. It can also thrive in vacant lots and industrial areas.
What does mullein look like?
Mullein has thick, densely hairy, grey-green leaves and tall, unbranched stems with yellow flowers at the top. Its fuzzy, green-gray rosettes of leaves and tall spikes of yellow flowers make it easy to identify.
Is mullein edible?
Yes, mullein is edible, but it is not very palatable and is best used for medicinal preparations such as infused oil, baths, ointments, and perfumes.
What is the optimal time for the harvest of mullein flowers and leaves?
The optimal time for the harvest of mullein flowers and leaves is during the summer when the plant is in bloom. This is when the plant’s medicinal properties are at their peak.
What are the potential health benefits of mullein tea?
Mullein tea offers potential health benefits such as aiding in expelling excess mucus, combating viral infections, decreasing inflammation, and providing cellular protection. Try incorporating it into your routine for its potential health-boosting properties.