Piracetam, the first nootropic drug, has long been a topic of interest for its potential cognitive-enhancing abilities and neuroprotective effects. But what exactly is piracetam, how does it work, and is it truly effective? This blog post will explore the origins, mechanisms, and potential applications of piracetam, along with its safety, side effects, and interactions with other medications. By the end of this post, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of this fascinating compound and its place in the world of cognitive enhancement.
Table of Contents
Short Summary
Piracetam is a nootropic drug developed to enhance cognitive function and provide neuroprotective properties.
Studies have suggested positive outcomes of piracetam therapy, Research is needed.
Consultation from a healthcare professional is essential for safe and effective use of this nootropic drug.
Understanding Piracetam: Origins and Functions
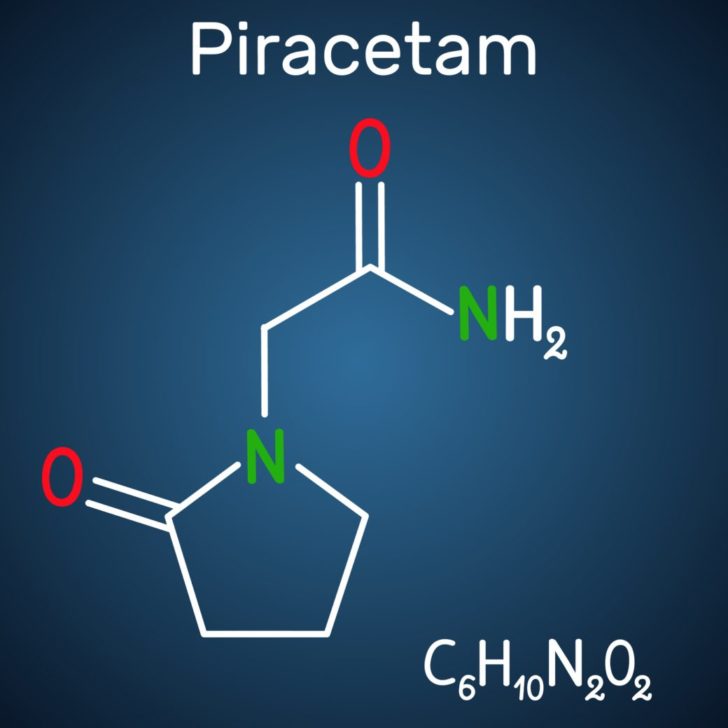
Piracetam is a synthetic derivative of GABA, a naturally occurring neurotransmitter in the brain. As a cyclic derivative of this essential chemical, piracetam was developed to enhance cognitive function and treat various neurological disorders. With the chemical name 2-oxo-1-pyrrolidine acetamide, piracetam is designed to address cognitive disorders and potentially provide neuroprotective and anticonvulsant properties.
The potential neuroprotective and anticonvulsant properties of piracetam are believed to stem from its interaction with phospholipid membranes and its role in restoring neurotransmission. In terms of pharmacokinetics, piracetam has a volume of distribution of approximately 0.6L/kg and a plasma half-life of about 5 hours, following oral or intravenous administration. Its safety profile is generally considered favorable, with minimal adverse effects reported.
As the first nootropic drug, piracetam has paved the way for further research and development of cognitive-enhancing compounds. While the precise mechanism of action remains elusive, piracetam’s potential benefits in cognitive function and neuroprotection continue to garner interest from both the scientific community and the general public.
Exploring the Mechanism of Action
Although the exact mechanism of action for piracetam is not yet fully understood, several hypotheses have been proposed. One such hypothesis involves interactions with phospholipid membranes, neurotransmission restoration, and improved microcirculation. By influence membrane function, piracetam is believed to exhibit its neuroprotective and anticonvulsant effects. Piracetam’s neuronal effects include increasing the density of postsynaptic receptors and/or restoring their function by stabilizing membrane fluidity. This may be how piracetam mediates neuroprotective effects. Additionally, piracetam has vascular effects, such as enhancing erythrocyte deformability, decreasing platelet aggregation, and reducing erythrocyte adhesion to the vascular endothelium.
These mechanisms contribute to the cognitive benefits observed with piracetam therapy, including enhanced learning, memory, attention, and consciousness. However, it is important to note that the precise mechanisms by which piracetam exerts its effects are still a topic of ongoing research and debate.
In summary, despite the lack of a definitive understanding of piracetam’s mechanism of action, the compound continues to pique interest due to its potential benefits in various cognitive processes and neuroprotection. Future research may provide further insights into the complex interactions and effects of this intriguing nootropic drug.
Assessing the Efficacy of Piracetam Therapy
The efficacy of piracetam therapy is a topic of ongoing discussion and research. Some studies have shown that piracetam is effective in improving cognitive function, myoclonus, vertigo, and reducing symptoms of tardive dyskinesia. However, the evidence supporting its use in the treatment of dementia or cognitive impairment is insufficient. Piracetam has been used to address conditions such as myoclonus, breath-holding spells in children, cognitive decline in aging, and sickle cell anemia. As for its efficacy in healthy individuals and those suffering from dementia, the results are not yet conclusive.
Despite the debate surrounding its efficacy, some studies have indicated positive outcomes on seizure frequency and cognitive function in aging individuals. However, more substantial evidence is required to form a definitive conclusion on the effectiveness of piracetam therapy.
In light of the existing research, it is crucial to approach piracetam therapy with caution and skepticism. While some studies have shown promising results, the overall effectiveness of piracetam in treating various conditions remains uncertain, and more rigorous research is needed.
Potential Applications of Piracetam
Piracetam has been utilized in various applications, including the piracetam treatment of myoclonus of cortical origin in adult patients and as a metabolic enhancer, piracetam ameliorates symptoms in some individuals. It is available in different oral formulations and has been used for medical or dietary use to address breath-holding spells in children and cognitive decline in aging.
However, the efficacy of piracetam for dementia and healthy individuals is yet to be conclusively determined. While some studies have shown potential vascular effects, such as piracetam decreases adhesion of erythrocytes to the vascular endothelium, the overall effectiveness of piracetam therapy in these populations remains uncertain.
It is important to recognize the potential limitations of the piracetam therapy and to approach its use with caution. While it has demonstrated some benefits in specific populations and conditions, its efficacy for dementia and healthy individuals is still a subject of ongoing research and debate.
In conclusion, piracetam has shown potential in various applications, but its efficacy for certain populations and conditions remains uncertain. As research continues, a clearer understanding of piracetam’s potential benefits and limitations will emerge, helping to inform future therapeutic approaches and applications.
Piracetam Safety and Side Effects
While piracetam is generally considered safe when taken in accordance with recommended dosages, it is not without potential side effects. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, weight gain, nervousness, and sleep changes. Additionally, there are certain contraindications for specific patient populations, such as those with severe kidney or liver disease, Huntington’s disease, or bleeding conditions. Piracetam should not be taken by women who are pregnant or breastfeeding, or by children unless under the guidance of a medical professional. In cases of acute, significant overdose, it is advised to empty the stomach either through gastric lavage or induced emesis, as there are no known antidotes for piracemam. Treatment for overdose must be implemented quickly, as the effects can be serious. Symptomatic treatment may be provided through hemodialysis.
It is recommended to discontinue use of piracetam at least two weeks prior to surgery, and to avoid abrupt withdrawal to ensure safe discontinuation. For individuals with specific health conditions, such as kidney issues, epilepsy, or cocaine use disorder, it is crucial to consult a healthcare provider before taking piracetam.
In conclusion, while piracetam is generally considered safe, it is essential to be aware of potential side effects, contraindications, and precautions. Consulting with a healthcare professional can help ensure safe and effective use of this nootropic drug.
Interactions with Other Medications
Piracetam may have interactions with certain medications. These include anticoagulants, blood thinners and thyroid supplements. These interactions may increase the risk of bleeding. It is important to discuss potential interactions with a healthcare provider before taking piracetam, especially if you are currently taking any medications that may interact with it.
While piracetam has no known severe or serious interactions with other drugs, it is still crucial to monitor for potential interactions and side effects. A healthcare professional can provide guidance on how to safely use piracetam and monitor for any potential interactions with other medications.
In summary, it is essential to be aware of potential interactions between piracetam and other medications. Consulting a healthcare professional can help ensure the safe and effective use of this nootropic drug in combination with other medications.
Alternative Nootropic Drugs
Several synthetic substances similar to piracetam have been developed, including levetiracetam, a more potent derivative of piracetam. Levetiracetam is available in the US and is marketed under various brand names as a treatment for partial onset seizures, myoclonic seizures, and tonic-clonic seizures.
In addition to levetiracetam, other alternative nootropic drugs exist, such as Adderall, Ritalin, Racetams, CDP-choline, L-theanine, creatine monohydrate, Bacopa monnieri, huperzine A, vinpocetine, and Vyvamind. These compounds, like piracetam, aim to enhance cognitive functioning and may offer potential benefits for various cognitive and neurological conditions.
As research continues to explore the potential benefits and mechanisms of action for these alternative nootropic drugs through human studies, individuals seeking cognitive enhancement may consider trying different compounds to determine which one best suits their needs and preferences, while referring to sources like cns drug rev for further information.
Piracetam Formulations and Brand Names
Piracetam is available in various formulations, including piracetam oral formulations, injections, and infusions. It is marketed under several brand names, such as Nootropil, Neurocetam, Neurofit, Normabrain, Cerecetam, Pirahenz, Sumocetam, and Alphacitam. Knowing the different formulations and brand names can help individuals seeking piracetam therapy find the most suitable option for their needs.
It is essential to consult a healthcare professional before starting any piracetam regimen to ensure safe and effective use.
Legal Status and Regulations
Piracetam’s legal status varies by country, with some requiring prescriptions while others allow over-the-counter purchases. In the United States, piracetam is not approved by the FDA for dietary supplements, but can be sold for research purposes. In some European countries, a prescription is necessary to purchase piracetam, while in others, it is available over the counter.
In Australia, piracetam can be obtained with a valid prescription. Additionally, it is also possible to import up to 3 months’ supply of the compound from suppliers outside of Australia under a “Personal Importation Scheme”. In Canada, it is not available for sale, but it can be imported for personal use.
It is crucial for individuals seeking piracetam therapy to be aware of the legal status and regulations in their country of residence. Consulting with a healthcare professional can help ensure that the use of piracetam is in compliance with local laws and guidelines.
Tips for Safe and Effective Piracetam Use
To ensure safe and effective use of piracetam, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for guidance on appropriate dosing, potential interactions, and monitoring of side effects. The recommended piracetam dosage range for adults is between 1,200 mg and 4,800 mg per day, with the suggestion to start with a lower dosage and gradually increase it as needed. Piracetam has a bitter taste, so swallowing the tablets whole is advised.
Be aware of potential side effects and interactions associated with piracetam, such as drowsiness, weakness, and coordination issues, and keep track of renal function and abstain from concurrent use with thyroid hormones.
In conclusion, consulting a healthcare professional and following their guidance on dosing, interactions, and monitoring of side effects is crucial for ensuring the safe and effective use of piracetam.
Learn more, visit 5 Benefits of Piracetam (Plus Side Effects)
Summary
Throughout this blog post, we have explored the origins, mechanisms, and potential applications of piracetam, as well as its safety, side effects, and interactions with other medications. While the efficacy of piracetam therapy remains a topic of ongoing research and debate, its potential cognitive-enhancing abilities and neuroprotective effects continue to generate interest.
With various alternative nootropic drugs available, individuals seeking cognitive enhancement have a range of options to consider. It is essential to consult a healthcare professional before starting any piracetam regimen or trying alternative nootropic drugs, to ensure safe and effective use.
As research continues to uncover the mysteries surrounding piracetam and its potential benefits, we can look forward to a future where cognitive enhancement and neuroprotection are more readily accessible and understood.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a piracetam used for?
Piracetam is a nootropic drug commonly used as a cognitive enhancer to improve memory, attention and learning. It is also marketed as a treatment for myoclonus and suggested uses include Alzheimer’s disease, dementia, stroke, deep vein thrombosis, tardive dyskinesia, and dyslexia.
Is piracetam illegal in the US?
Piracetam is not illegal in the United States, though it is not approved or regulated by the FDA as a dietary supplement. It can be purchased from a number of online suppliers but may require a prescription in certain countries such as Australia.
How does piracetam affect the brain?
Piracetam improves the function of neurotransmitters, such as acetylcholine and glutamate, which are involved in memory processes. It also has neuroprotective and anticonvulsant properties, making cell membranes more fluid and improving communication between cells.
Research suggests that taking piracetam may enhance brain function.
What type of drug is piracetam?
Piracetam is a man-made nootropic drug developed in the 1960s used to enhance memory, learning, and other cognitive functions. It belongs to the racetam class of drugs and has been used to treat conditions like myoclonus, sickle cell disease, and alcohol dependence.
What is piracetam, and how does it work?
Piracetam is a synthetic derivative of GABA designed to improve cognitive functioning and treat neurological disorders. Its action is believed to involve interactions with phospholipid membranes, neurotransmission restoration, and improved microcirculation.
It has been used to treat a variety of conditions, including Alzheimer’s disease, dementia, and stroke. It has also been used to improve memory, concentration, and learning. Studies.